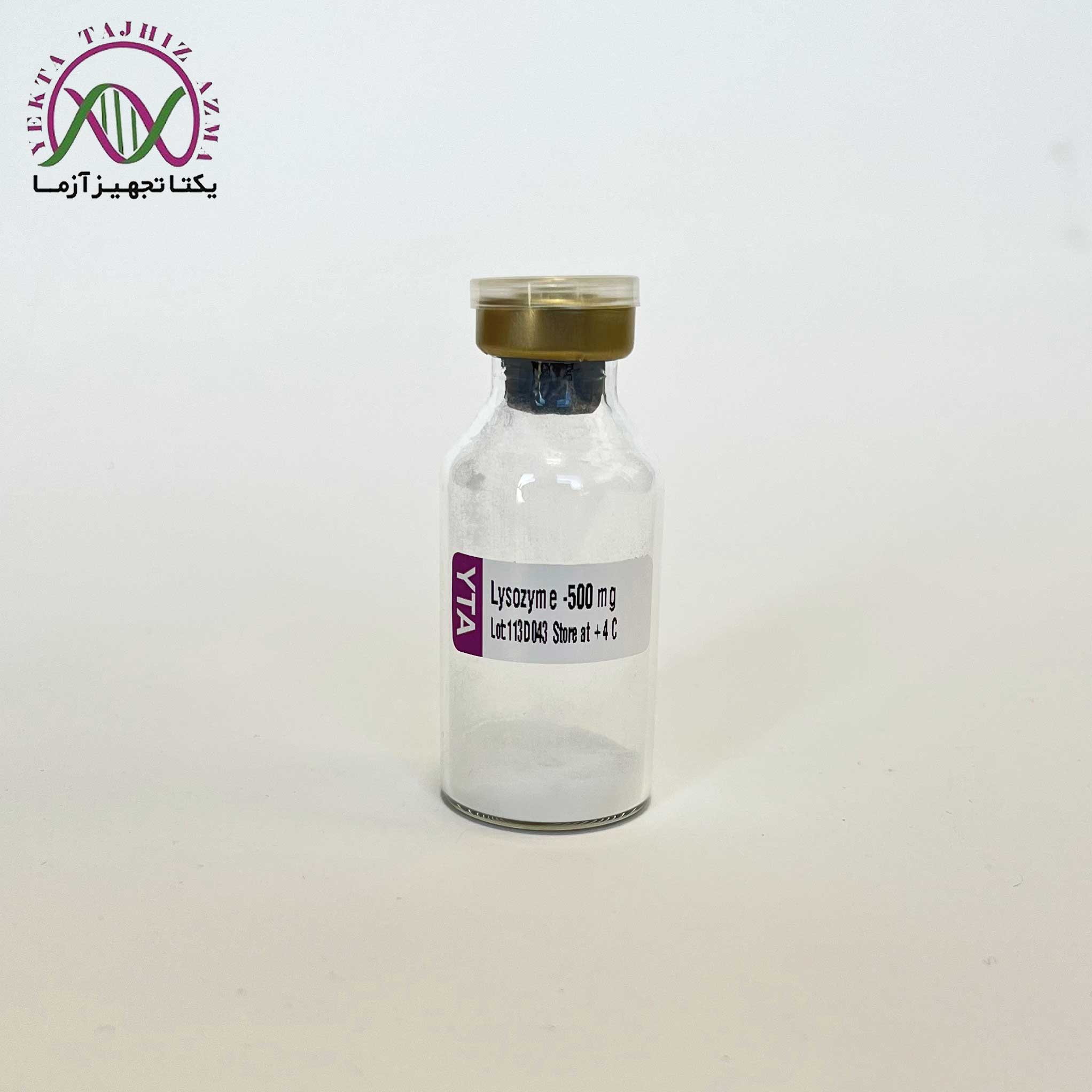
Lysozyme
Features:
- Improve efficiency of protein or DNA/RNA extraction
- RNase and DNase free
- Enzyme for lysis of bacterial cell walls
Lysozyme is an enzyme used for the extraction of proteins and nucleic acid from bacteria. Lysozyme is an enzyme characterized by the ability to break down the bacterial cell wall by hydrolyzing the peptidoglycan present in the cell walls. Gram-positive cells are quite susceptible to this hydrolysis as their cell walls have a high proportion of peptidoglycan. It hydrolyzes ß (1-4) linkages between N-acetyl muraminic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in peptidoglycan and between N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in chitodextrin.
Lysozyme has an antibacterial effect on Gram-positive bacteria, aerobic spore forming bacteria, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, and the like, and does not adversely affect human cells without cell walls. Lysozyme can also bind directly to negatively charged viral proteins, forming complex salts with DNA, RNA, and apoproteins, inactivating viruses. Therefore, the enzyme has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral and the like. This lysozyme preparation is purified from chicken egg white, crystallized three times, dialyzed, and supplied as a lyophilized powder. It is suitable for use as a lysing agent in the purification of plasmid DNA using a boiling lysing technique.